A system mechanism controls access to an object (ex. military environment)
Individual users cannot control
This prevents people with high clearance from sharing information by only allowing them to "write up" but not "write down". While "read down" seems intuitive, the non-intuitive "write up" rule is quite important for security to prevent information leakage.
Bell LaPadula model
Not that important
Security Clearances and Classifications
- L(S) = lS: The security clearance level of a subject S (e.g., a user or a process).
- L(O) = lO: The security classification of an object O (e.g., a file or a database entry).
Security Conditions
Simple-Security Condition
also known as the "no read up" or "ss-property"
- A subject S can read an object O if and only if the security classification of O (lO) is less than or equal to the security clearance of S (lS), and S has discretionary read access to O.
- This rule ensures that a subject cannot read data at a higher security level than its own, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
*-Property
Star Property, also known as the "no write down" or "write-up" policy
- A subject S can write to an object O if and only if the security clearance of S (lS) is less than or equal to the security classification of O (lO), and S has discretionary write access to O.
- This rule is designed to prevent data from being moved from a higher security level to a lower one, avoiding the potential leak of sensitive information to less secure areas.
A lattice is a mathematical structure that represents the ordering of subsets, used to define relationships between elements. Particularly in security models or type systems, lattice structures are utilized to express relationships between various security levels or types. Here, "meet" and "join" are operations that represent the relationship between two elements in a lattice. (Lattice Theory)
Partially-ordered set (a.k.a. Poset) where every pair has the greatest lower bound (meet) and least upper bound (join)
Meet (⊓)
By meet operation, we can prevent unlimited information propagation
The meet operation represents the maximum lower bound or intersection point of two elements. For two elements A and B, the meet of A and B is the largest element that is less than or equal to both A and B. In a security context, the result of a meet operation between two security levels can represent the highest security level at which information can be safely shared between both levels.
Join (⊔)
The join operation represents the minimum upper bound or union of two elements. For two elements A and B, the join of A and B is the smallest element that is greater than or equal to both A and B. In a security context, the result of a join operation between two security levels means the lowest security level that can safely handle information from either of the two levels.
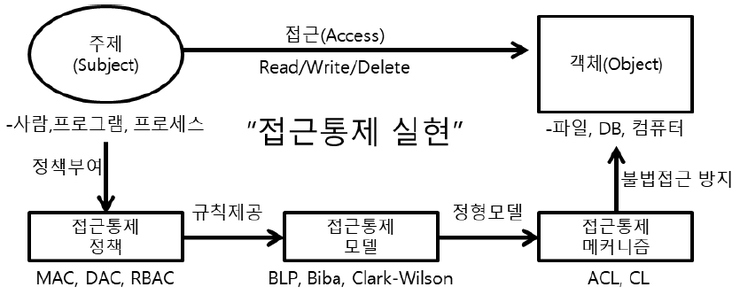
접근통제 모델(BLP, Biba, Clark-Wilson)
q 접근통제 개요 - 접근통제는 사용자(주체)의 신원을 식별/인증하여...
https://m.blog.naver.com/sdug12051205/221575582613

 Seonglae Cho
Seonglae Cho