Particles without mass, in the general definition, also have their acceleration impeded by the Higgs field, slowing their movement.
The degree to which the particle is hindered varies depending on the intensity of the interaction, and the mass of the particle is determined by this interaction.
This means that mass is not an essential quantity as Newton predicted, but a secondary characteristic due to the interaction with the Higgs field.
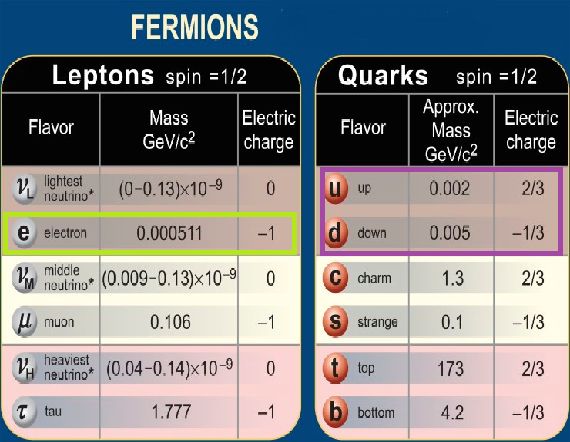
In 1967, Weinberg introduced a Higgs field with four components. Three of them are W+, W-, and Z0, and the remaining one is the Higgs boson with spin 0.
On July 4, 2012, CERN scientists discovered a particle believed to be a Higgs boson using the Large Hadron Collider. This particle's mass was 133 times that of a proton, and it exchanged interactions with other particles in the way Peter Higgs predicted. It is more important to find out what kind of Higgs boson this particle is, and it has been proven that at least one type of Higgs field exists.
The currently discovered Higgs particle plays a role in giving mass related to weak nuclear force to particles, and this has an indirect relationship with gravity. Supersymmetry predicts the existence of at least five types of Higgs bosons, which could help explain phenomena such as the quantum explanation of gravity, the dark matter problem in the universe, the asymmetry between matter and antimatter, and the inflation of the early universe.
신의입자 "힉스"---힉스장이론
약전자기 시기가 끝날 무렵, 우주가 1015K까지 식으면서 힉스장이 고정된 ...
https://blog.naver.com/sdkim1004/220999556537

 Seonglae Cho
Seonglae Cho