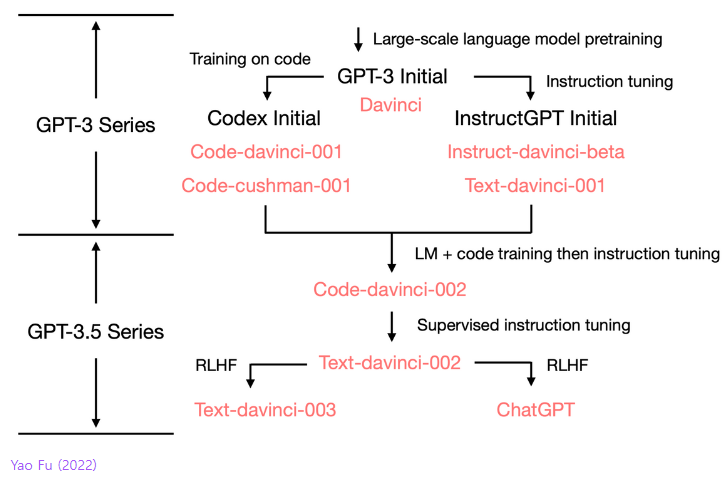
Reinforcement learning from human feedback
Learn reward functions based on human feedback and use them to update policies\
- Create human preference ranking data
- Build an external reward model from this data
- Train the LLM using PPO with these rewards as labels
- The internal critic differs from the external critic
- A critic is needed because reward models alone can't be used for RL due to lack of gradients
This approach is necessary because human data alone is insufficient and for data scaling purposes
Some of fancy way like below Language Model RL or just same as pre-training by well selected data
Basically reward model

with PPO


Limitation
RLHF still cannot fundamentally solve LM's core issues such as model size and hallucination, and the approach is complex
LLaVA-RLHF
LLaVA-RLHF
Visual Instruction Tuning
https://llava-rlhf.github.io/
Multi Adapter RL (MARL) - a single base model for everything
We’re on a journey to advance and democratize artificial intelligence through open source and open science.
https://huggingface.co/docs/trl/multi_adapter_rl
RLHF란?
RLHF에 대해 알아보자
https://velog.io/@nellcome/RLHF란
Reinforcement learning from human feedback
In machine learning, reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) or reinforcement learning from human preferences is a technique that trains a "reward model" directly from human feedback and uses the model as a reward function to optimize an agent's policy using reinforcement learning (RL) through an optimization algorithm like Proximal Policy Optimization.[1][2] The reward model is trained in advance to the policy being optimized to predict if a given output is good (high reward) or bad (low reward). RLHF can improve the robustness and exploration of RL agents, especially when the reward function is sparse or noisy.[3]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reinforcement_learning_from_human_feedback
OOD generalization is crucial given the wide range of real-world scenarios in which these models are being used, while output diversity refers to the model’s ability to generate varied outputs and is important for a variety of use cases
RLHF generalizes better than SFT to new inputs, particularly as the distribution shift between train and test becomes larger. However, RLHF significantly reduces output diversity compared to SFT across a variety of measures, implying a tradeoff in current LLM fine-tuning methods between generalization and diversity.
arxiv.org
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.06452
criticize
arxiv.org
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.16349
Deep Dive into LLMs like ChatGPT
This is a general audience deep dive into the Large Language Model (LLM) AI technology that powers ChatGPT and related products. It is covers the full training stack of how the models are developed, along with mental models of how to think about their "psychology", and how to get the best use them in practical applications. I have one "Intro to LLMs" video already from ~year ago, but that is just a re-recording of a random talk, so I wanted to loop around and do a lot more comprehensive version.
Instructor
Andrej was a founding member at OpenAI (2015) and then Sr. Director of AI at Tesla (2017-2022), and is now a founder at Eureka Labs, which is building an AI-native school. His goal in this video is to raise knowledge and understanding of the state of the art in AI, and empower people to effectively use the latest and greatest in their work.
Find more at https://karpathy.ai/ and https://x.com/karpathy
Chapters
00:00:00 introduction
00:01:00 pretraining data (internet)
00:07:47 tokenization
00:14:27 neural network I/O
00:20:11 neural network internals
00:26:01 inference
00:31:09 GPT-2: training and inference
00:42:52 Llama 3.1 base model inference
00:59:23 pretraining to post-training
01:01:06 post-training data (conversations)
01:20:32 hallucinations, tool use, knowledge/working memory
01:41:46 knowledge of self
01:46:56 models need tokens to think
02:01:11 tokenization revisited: models struggle with spelling
02:04:53 jagged intelligence
02:07:28 supervised finetuning to reinforcement learning
02:14:42 reinforcement learning
02:27:47 DeepSeek-R1
02:42:07 AlphaGo
02:48:26 reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF)
03:09:39 preview of things to come
03:15:15 keeping track of LLMs
03:18:34 where to find LLMs
03:21:46 grand summary
Links
- ChatGPT https://chatgpt.com/
- FineWeb (pretraining dataset): https://huggingface.co/spaces/HuggingFaceFW/blogpost-fineweb-v1
- Tiktokenizer: https://tiktokenizer.vercel.app/
- Transformer Neural Net 3D visualizer: https://bbycroft.net/llm
- llm.c Let's Reproduce GPT-2 https://github.com/karpathy/llm.c/discussions/677
- Llama 3 paper from Meta: https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.21783
- Hyperbolic, for inference of base model: https://app.hyperbolic.xyz/
- InstructGPT paper on SFT: https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02155
- HuggingFace inference playground: https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface/inference-playground
- DeepSeek-R1 paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.12948
- TogetherAI Playground for open model inference: https://api.together.xyz/playground
- AlphaGo paper (PDF): https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10045895/1/agz_unformatted_nature.pdf
- AlphaGo Move 37 video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HT-UZkiOLv8
- LM Arena for model rankings: https://lmarena.ai/
- AI News Newsletter: https://buttondown.com/ainews
- LMStudio for local inference https://lmstudio.ai/
- The visualization UI I was using in the video: https://excalidraw.com/
- The specific file of Excalidraw we built up: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EZh5hNDzxMMy05uLhVryk061QYQGTxiN/view?usp=sharing
- Discord channel for Eureka Labs and this video: https://discord.gg/3zy8kqD9Cp
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7xTGNNLPyMI&t=2h53m

 Seonglae Cho
Seonglae Cho