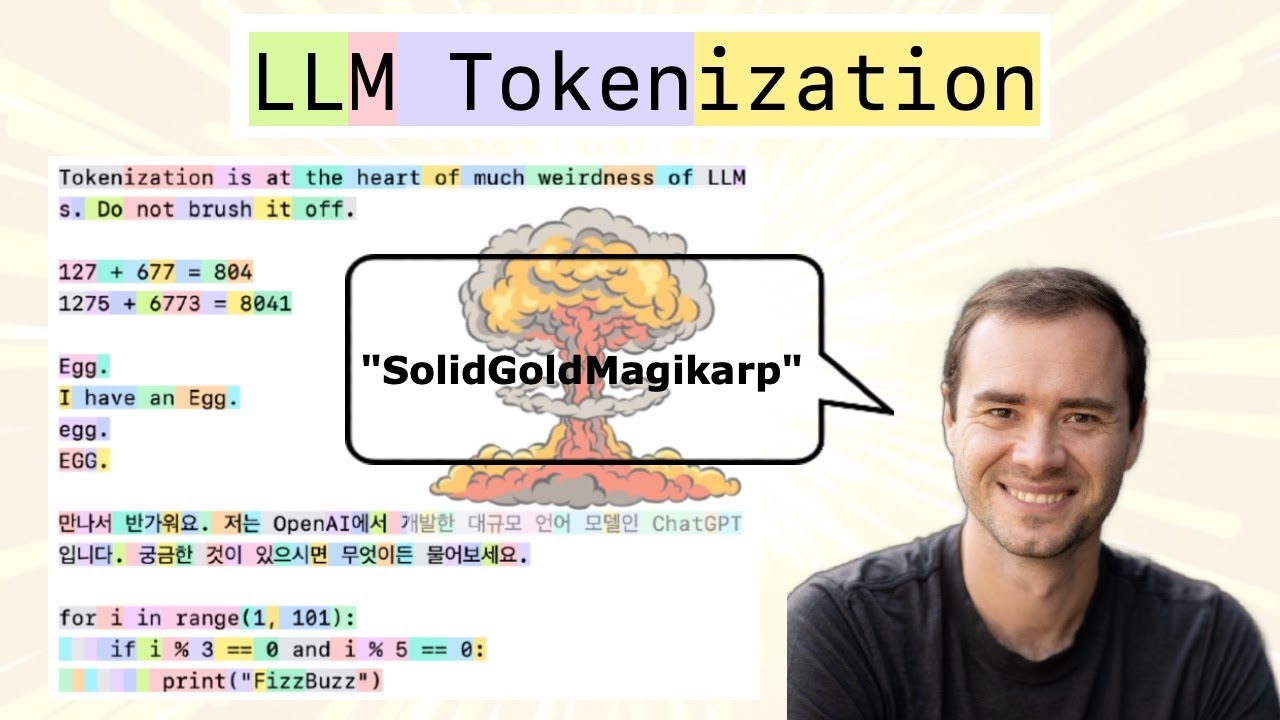
Tokenization is not neutral preprocessing, but a strong Inductive Bias
Even though simple algorithms like BPE scale well with token sets in large datasets and work well in large models, the simplicity of tokenizers can create a bottleneck where high-level tokens cause performance issues in complex reasoning or arithmetic. This may require optimization with Text Tokenizer Training for LLMs.
While Longest prefix matching based encoding provides lightweight inference costs, some greedy encoding or more complex algorithms might be more fundamentally suitable for language modeling.
Text tokenizing, similar to Text Compression, is crucial for effectively encoding text corpus by breaking it down into meaningful, recurring tokens.
According to Karpathy, most problems in LLMs originate from tokenization issues. This is why research is increasingly focusing on Tokenizer Substitute.
Text Tokenizer Notion
Text Tokenizer Libraries
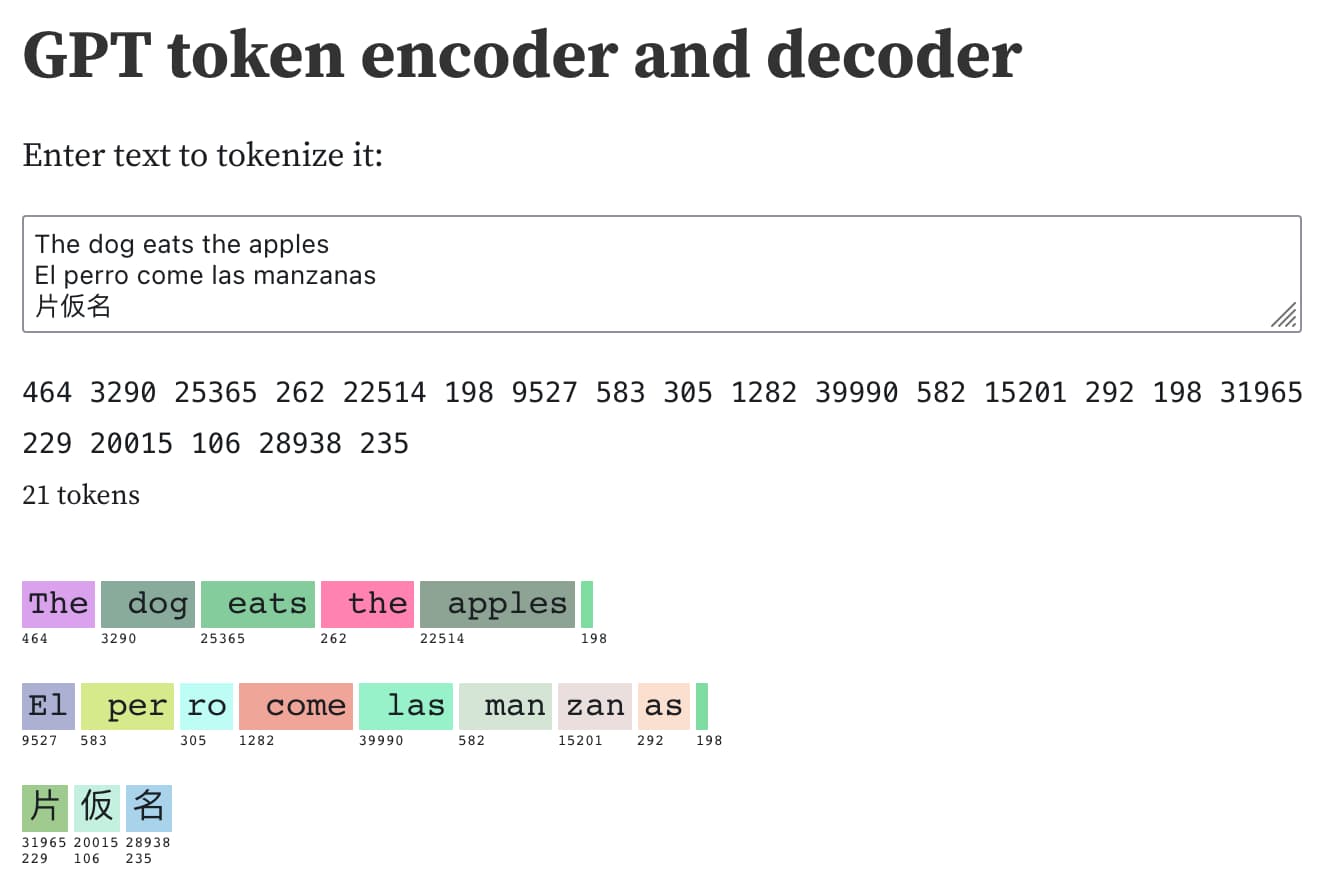
Test openai tokenizer
OpenAI Platform
Explore developer resources, tutorials, API docs, and dynamic examples to get the most out of OpenAI's platform.
https://platform.openai.com/tokenizer

Understand
Let's build the GPT Tokenizer
The Tokenizer is a necessary and pervasive component of Large Language Models (LLMs), where it translates between strings and tokens (text chunks). Tokenizers are a completely separate stage of the LLM pipeline: they have their own training sets, training algorithms (Byte Pair Encoding), and after training implement two fundamental functions: encode() from strings to tokens, and decode() back from tokens to strings. In this lecture we build from scratch the Tokenizer used in the GPT series from OpenAI. In the process, we will see that a lot of weird behaviors and problems of LLMs actually trace back to tokenization. We'll go through a number of these issues, discuss why tokenization is at fault, and why someone out there ideally finds a way to delete this stage entirely.
Chapters:
00:00:00 intro: Tokenization, GPT-2 paper, tokenization-related issues
00:05:50 tokenization by example in a Web UI (tiktokenizer)
00:14:56 strings in Python, Unicode code points
00:18:15 Unicode byte encodings, ASCII, UTF-8, UTF-16, UTF-32
00:22:47 daydreaming: deleting tokenization
00:23:50 Byte Pair Encoding (BPE) algorithm walkthrough
00:27:02 starting the implementation
00:28:35 counting consecutive pairs, finding most common pair
00:30:36 merging the most common pair
00:34:58 training the tokenizer: adding the while loop, compression ratio
00:39:20 tokenizer/LLM diagram: it is a completely separate stage
00:42:47 decoding tokens to strings
00:48:21 encoding strings to tokens
00:57:36 regex patterns to force splits across categories
01:11:38 tiktoken library intro, differences between GPT-2/GPT-4 regex
01:14:59 GPT-2 encoder.py released by OpenAI walkthrough
01:18:26 special tokens, tiktoken handling of, GPT-2/GPT-4 differences
01:25:28 minbpe exercise time! write your own GPT-4 tokenizer
01:28:42 sentencepiece library intro, used to train Llama 2 vocabulary
01:43:27 how to set vocabulary set? revisiting gpt.py transformer
01:48:11 training new tokens, example of prompt compression
01:49:58 multimodal [image, video, audio] tokenization with vector quantization
01:51:41 revisiting and explaining the quirks of LLM tokenization
02:10:20 final recommendations
02:12:50 ??? :)
Exercises:
- Advised flow: reference this document and try to implement the steps before I give away the partial solutions in the video. The full solutions if you're getting stuck are in the minbpe code https://github.com/karpathy/minbpe/blob/master/exercise.md
Links:
- Google colab for the video: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1y0KnCFZvGVf_odSfcNAws6kcDD7HsI0L?usp=sharing
- GitHub repo for the video: minBPE https://github.com/karpathy/minbpe
- Playlist of the whole Zero to Hero series so far: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VMj-3S1tku0&list=PLAqhIrjkxbuWI23v9cThsA9GvCAUhRvKZ
- our Discord channel: https://discord.gg/3zy8kqD9Cp
- my Twitter: https://twitter.com/karpathy
Supplementary links:
- tiktokenizer https://tiktokenizer.vercel.app
- tiktoken from OpenAI: https://github.com/openai/tiktoken
- sentencepiece from Google https://github.com/google/sentencepiece
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zduSFxRajkE
You Should Probably Pay Attention to Tokenizers
Last week I was helping a friend of mine to get one of his new apps off the ground. I can’t speak much about it at the moment, other than like most apps nowadays it has some AI sprinkled over …
https://cybernetist.com/2024/10/21/you-should-probably-pay-attention-to-tokenizers/
Understanding GPT tokenizers
Large language models such as GPT-3/4, LLaMA and PaLM work in terms of tokens. They take text, convert it into tokens (integers), then predict which tokens should come next. Playing …
https://simonwillison.net/2023/Jun/8/gpt-tokenizers/
Tokenizer Arena
Tokenizer Arena - a Hugging Face Space by Cognitive-Lab
Discover amazing ML apps made by the community
https://huggingface.co/spaces/Cognitive-Lab/Tokenizer_Arena

When adding new tokens (Not actually tokenizer part, but embedding layer)
- Average of existing embedding combinations
- A better method is using context vectors from the same model with LM head removed
Initializing New Word Embeddings for Pretrained Language Models · John Hewitt
This problem has been observed in huggingface issues (1) (2), and averaging has been proposed as a workaround by Eric Mitchell (and anecdotally by others); this blog post argues averaging should be the new “default” and provides some math to explain the problem and show why averaging is a good solution.
https://nlp.stanford.edu/~johnhew/vocab-expansion.html?fbclid=IwAR2EzF3t7m5ieDNKq6ltz7B-HXPIvU9Y8CUzVyAu44gW4NFq7Len6HUl0ww

 Seonglae Cho
Seonglae Cho