AI Wars
2006 - CUDA - Parallel processing
NVIDIA GPUs were originally designed for graphics rendering, but their architecture turned out to be perfectly suited for HPC (High-Performance Computing). Until the early 2000s, the computing industry's basic assumption was: performance improvement = clock speed increase (frequency scaling). Most programs were based on single-threaded serial computation. However, between 2003–2005, two things hit simultaneously: CPU heat and power limitations (the power wall). Around 4GHz, systems reached the thermal wall. CUDA was announced in 2006, introduced in 2007, and experienced explosive growth after AlexNet in 2012.
2012 AlexNet
Geoffrey Hinton, Ilya Sutskever, and Alex Krizhevsky trained AlexNet using GPUs. Using 2 GPUs, they successfully trained a large-scale CNN on ImageNet (1.2 million images) for the first time, revolutionizing computer vision performance.
2016 GPU supercomputer
After AlexNet in 2012, 2014–2016 marked the first deep learning boom as the entire industry shifted to CUDA. Jensen Huang recognized this potential and connected with Professor Hinton's team. After massive investment at NVIDIA, they unveiled the DGX-1 deep learning supercomputer at the GTC 2016 event three years later. However, the market didn't understand that "NVIDIA was becoming an AI company" the audience was quiet, there were no purchase requests, and the stock price plummeted.
Elon Musk approached them at that moment, saying his non-profit wanted to buy one. A non-profit buying a $120,000 supercomputer? Eager to make any sale, they boxed one up at headquarters and rushed it to San Francisco. Peter Abeel, Dario Amodei, Ilya Sutskever – the world's top young geniuses were gathered in a cramped second-floor office, and Jensen opened the box to deliver it. This was the beginning of everything. That photo of delivering the GPU to OpenAI. Elon looking down with his arms crossed, smiling.


Anyone can imagine how grateful Jensen must have been to Elon. In October 2025, Jensen delivered the latest model, DGX-Spark, to SpaceX – a device with compute power similar to DGX-1 but now shrunk to the size of a book.

As Jensen said, xAI will become the company that builds data centers with new chips the fastest. In this respect, xAI has an advantage.
2017 Transformer Model
To use the increased compute more efficiently, the Transformer architecture was proposed, enabling parallel token learning instead of time-dependent RNN structures. This marked the beginning of serious exploration into meta-learning and general intelligence.
2020 AI Scaling
OpenAI, with sufficient compute resources, was the first to release GPT-1, 2, and 3 with autoregressive insights and scaling, observing induced intelligence. They focused on scaling at the pretraining stage.
2022 ChatGPT
By applying RLHF, AI became truly useful for users for the first time, dramatically expanding the user base. Massive amounts of inference responses began accumulating, which became the foundation for rough test-time RL in the form of feedback.
2025 Reasoning Model
With NVIDIA's Blackwell deployment delays reducing chip compute scaling, test-time scaling similar to GRPO began with DeepSeek. Inference scaling compensated for the missing scaling dimension. Simultaneously, OpenAI, which had dominated pretraining hegemony, had to slow down, and xAI, Google, and Anthropic rose to form a four-way competition. With inference-time reasoning becoming critical for agents, companies with abundant inference resources like Google and Amazon-backed Anthropic established a competitive structure.
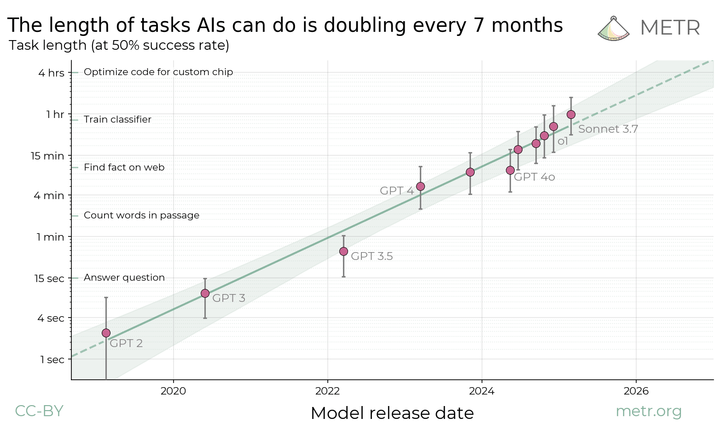
Measuring AI Ability to Complete Long Tasks
We propose measuring AI performance in terms of the *length* of tasks AI agents can complete. We show that this metric has been consistently exponentially increasing over the past 6 years, with a doubling time of around 7 months. Extrapolating this trend predicts that, in under a decade, we will see AI agents that can independently complete a large fraction of software tasks that currently take humans days or weeks.
https://metr.org/blog/2025-03-19-measuring-ai-ability-to-complete-long-tasks/
2025 Andrej Karpathy Vibe Coding
RLVR Emergence: Long-duration RL with automated verification rewards instead of human feedback → Jagged Intelligence: LLMs become dramatically smarter only in specific verifiable domains → Intelligence 'jaggedness' → Declining benchmark reliability → Claude Code: A turning point where local agents prove more practical than cloud-based solutions.
2025 LLM Year in Review
2025 Year in Review of LLM paradigm changes
https://karpathy.bearblog.dev/year-in-review-2025/

OpenRouter accounts for 1% of API usage but approximately shows market share
LLM Rankings | OpenRouter
Language models ranked and analyzed by usage across apps
https://openrouter.ai/rankings
The Inside Story of How Altman and Musk Went From Friends to Bitter Enemies
The two tech titans are in the meanest fight in business. The stakes couldn’t be higher.
https://www.wsj.com/tech/elon-musk-sam-altman-relationship-6889a77a


 Seonglae Cho
Seonglae Cho