stanford video
Computational Motifs (Stanford lecture 2) - Jack Merullo
What algorithmic primitives do transformers use? Certain "computational motifs" show up over and over again when we do interpretability on different models, tasks, and circuits.
Jack Merullo (Goodfire) gives a guest lecture on these computational motifs, and how can they help us understand models in more generalizable ways, in Surya Ganguli's Stanford course APPPHYS 293.
00:53 - Intro: defining "computational motifs"
05:48 - Induction heads (a classic motif)
08:31 - Motifs in the Indirect Object Identification circuit
44:33 - More examples
51:15 - Challenges and open problems
1:03:12 - Conclusion & questions
Read more about our research: https://www.goodfire.ai/research
Follow us on X: https://x.com/GoodfireAI
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cx3JlXDwMaU

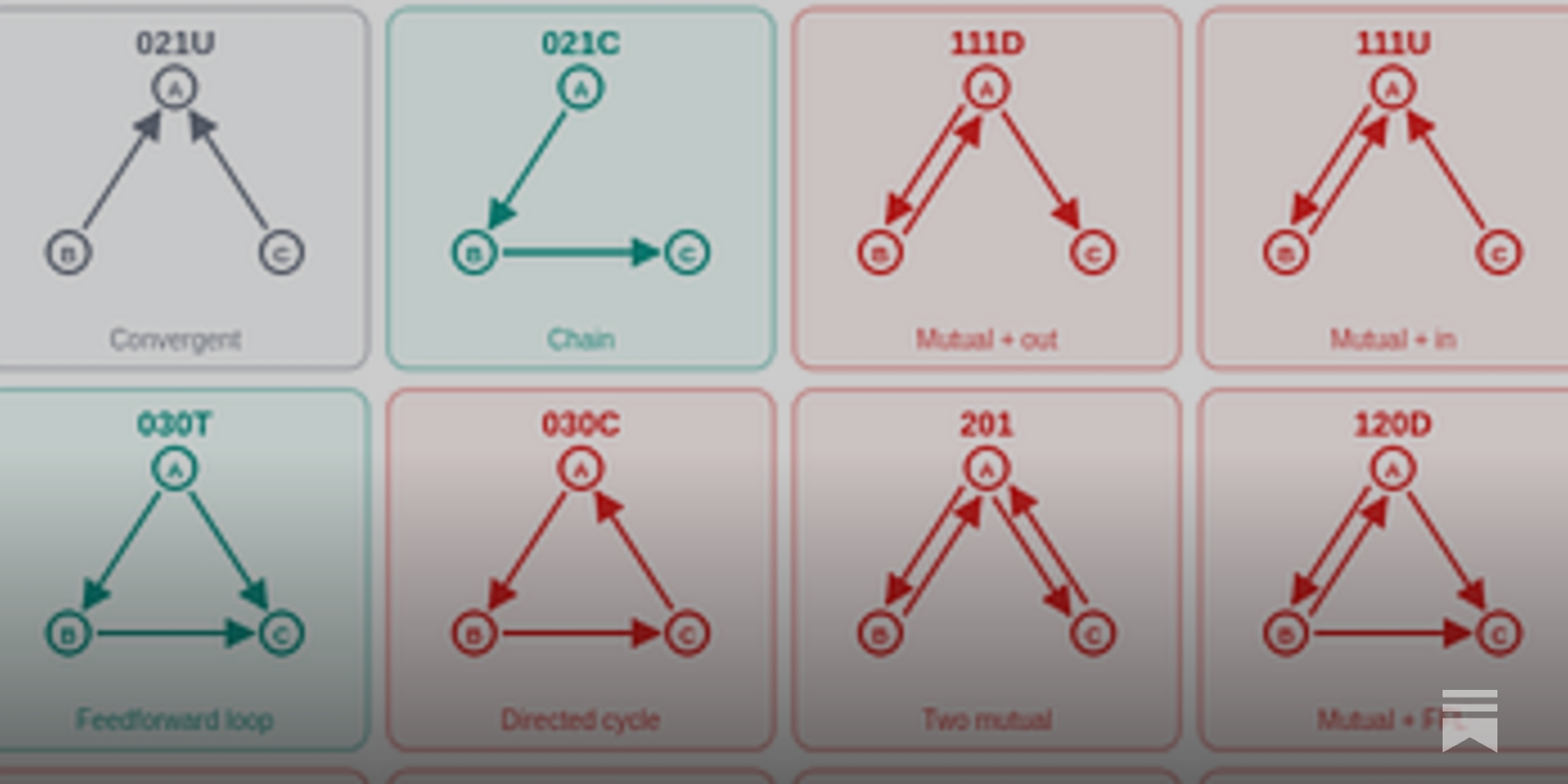
Network Motif Computational Motif
To automate attribution graph analysis, the tool circuit-motifs was created by applying network motif analysis from biology to LLM circuit interpretation. Analyzing 99 attribution graphs from Neuronpedia revealed that Feedforward Loop (FFL) structures overwhelmingly dominate in nearly all graphs. FFLs and simple chain structures are abundant, while cycle structures are nearly absent. Tracing individual FFLs reveals an actual step-by-step reasoning pipeline:
- Input concept extraction (grounding)
- Entity resolution
- Output competition and inhibition
Even with different models (Claude, Gemma, Qwen) or transcoder architectures, the FFL-centered pattern is largely preserved. Attribution graphs have a universal "structural grammar," which can be automatically summarized and compared through motif analysis.
Borrowing a tool from systems biology for mechanistic interpretability
TL;DR: I have been analyzing attribution graphs manually and found it to be tedious and hard to scale.
https://open2interp.substack.com/p/applying-network-motif-analysis-to

 Seonglae Cho
Seonglae Cho