Neural Plasticity
The brain's ability to reorganize its Neuron circuits independently, and proof that we have the power to make choices that shape our future life
Childhood violence causes the hippocampus to shrink and the amygdala to enlarge, leading to antisocial behaviors like violence or falling in love with abusive partners. Adolescence is a period of brain reconstruction, during which various standards change. In adulthood, it takes more effort to change these patterns. Our brains continue to change even after childhood and adolescence, influenced by culture and society, affected by the thought and emotional patterns of those around us. As time passes, this has an increasingly greater impact than everything that came before.
- Learning creates permanent changes in the brain
- Physical activities like exercise and dancing also promote neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity Types
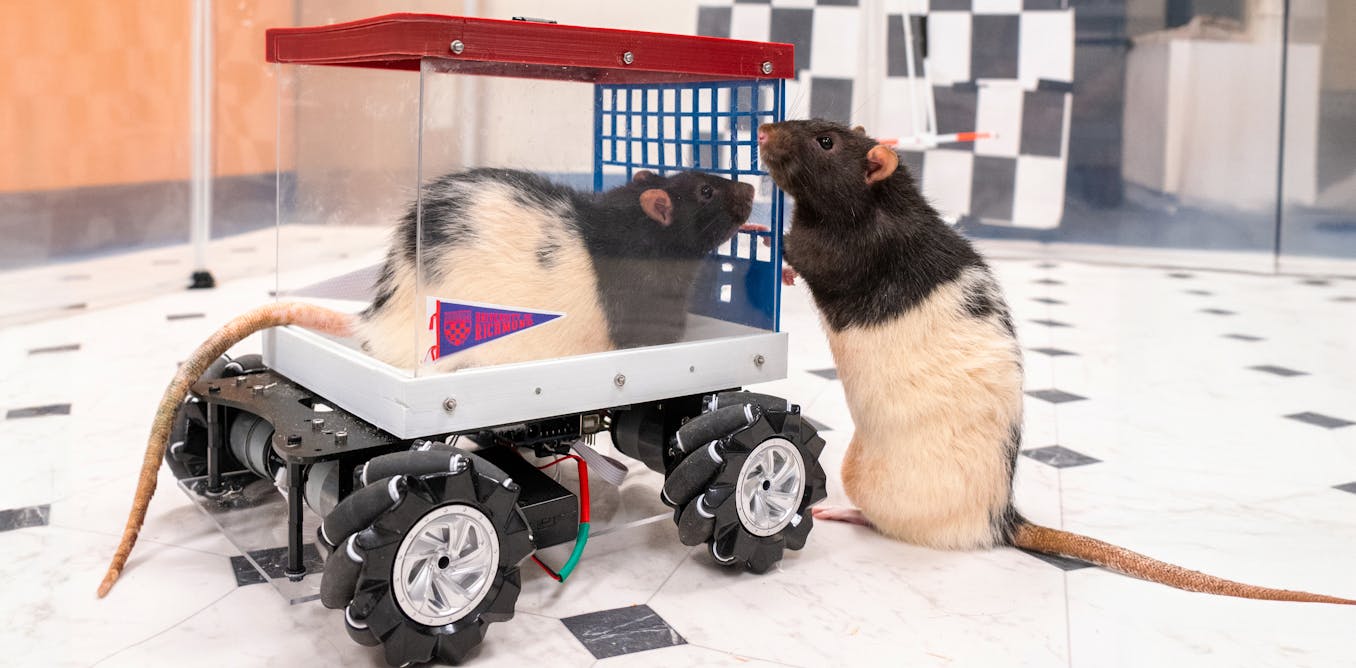
The finding supports the idea that complex environments enhance neuroplasticity. It suggests that anticipating positive experiences may help drive Persistence to keep searching for life's rewards.
I’m a neuroscientist who taught rats to drive − their joy suggests how anticipating fun can enrich human life
Equipped with a rodent version of a Cybertruck, these driving rats reveal that positive experiences may sculpt the brain just as powerfully as stressful ones
https://theconversation.com/im-a-neuroscientist-who-taught-rats-to-drive-their-joy-suggests-how-anticipating-fun-can-enrich-human-life-239029

AI
Neuroplasticity in LLMs
Advances in model editing promise to remove undesirable concepts from large language models by pruning neurons. Is this method of model editing truly robust? Can models recover unwanted concepts after pruning - and if so, how?
https://www.apartresearch.com/r/ai-neuroplasticity

지금부터라도 꽤 괜찮은 어른이 되는 법 | 성인의 뇌를 바꾸는 방법, 신경 가소성
#뇌과학 #신경가소성 #장동선
'나'라는 인간은 다양한 요인들로 복합적으로 형성된 복잡한 존재입니다.
그렇다면 어느 시기에 어떤 경험을 하는 것이 나라는 존재가 만들어지는 데 결정적인 영향을 줄까요?
아동기와 청소년기를 거쳐 어른이 된 우리의 뇌를 바꿀 수 있는 방법이 있을까요?
🧠 타임라인
00:00 시작
01:36 뇌의 형성에 가장 중요한 경험
05:09 청소년기
06:25 성인의 뇌를 변화시키는 법
08:42 삶을 행복하게 만드는 법
https://youtu.be/P7JJ6WtIKaQ?si=HKGsOLL1kHPTZj11

Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity, or brain plasticity, is the ability of neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization. It is when the brain is rewired to function in some way that differs from how it previously functioned.[1] These changes range from individual neuron pathways making new connections, to systematic adjustments like cortical remapping or neural oscillation. Other forms of neuroplasticity include homologous area adaptation, cross modal reassignment, map expansion, and compensatory masquerade.[2] Examples of neuroplasticity include circuit and network changes that result from learning a new ability, information acquisition, environmental influences, practice, and psychological stress.[3][4][5][6][7][8]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroplasticity
 Seonglae Cho
Seonglae Cho
