LLM Memory (Overfitting)
The real competitive advantage of AI services comes from accumulating data as users interact with the system, creating an implicit profile that generates a lock-in effect. (Enshittification)
To ultimately become like humans, knowledge needs to be distributed in vector space, but since performing weight training at every moment is too inefficient, we will likely need a separate storage system like Vector Database or Fast Weight.
AI Memory Mechanism is distinguished from AI Reasoning mechanism. While these two processes support each other, they remain separate. Through neuron activation classification probes, we can classify memorized tokens from non-memorized tokens with over 99.9% accuracy. Additionally, it's possible to effectively remove the memory mechanism by suppressing neuron activation patterns that depend on memorized data. Research has discovered that specific neurons (e.g., neuron 1668) play a crucial role in representing the model's confidence.
While Attention Mechanism implemented and mimiced Working memory(Short Term Memory) effectively, Long Term Memory implementation is not incorporated. KV matching is a memory write operation while query is a read operation.
From a product perspective, memory is personal data that is not shared between platforms and other providers. This will be a significant moat and a business asset that prevents users from leaving the platform.
dynamically saving prompt, dynamic skills, static rules, dynamic memory all different
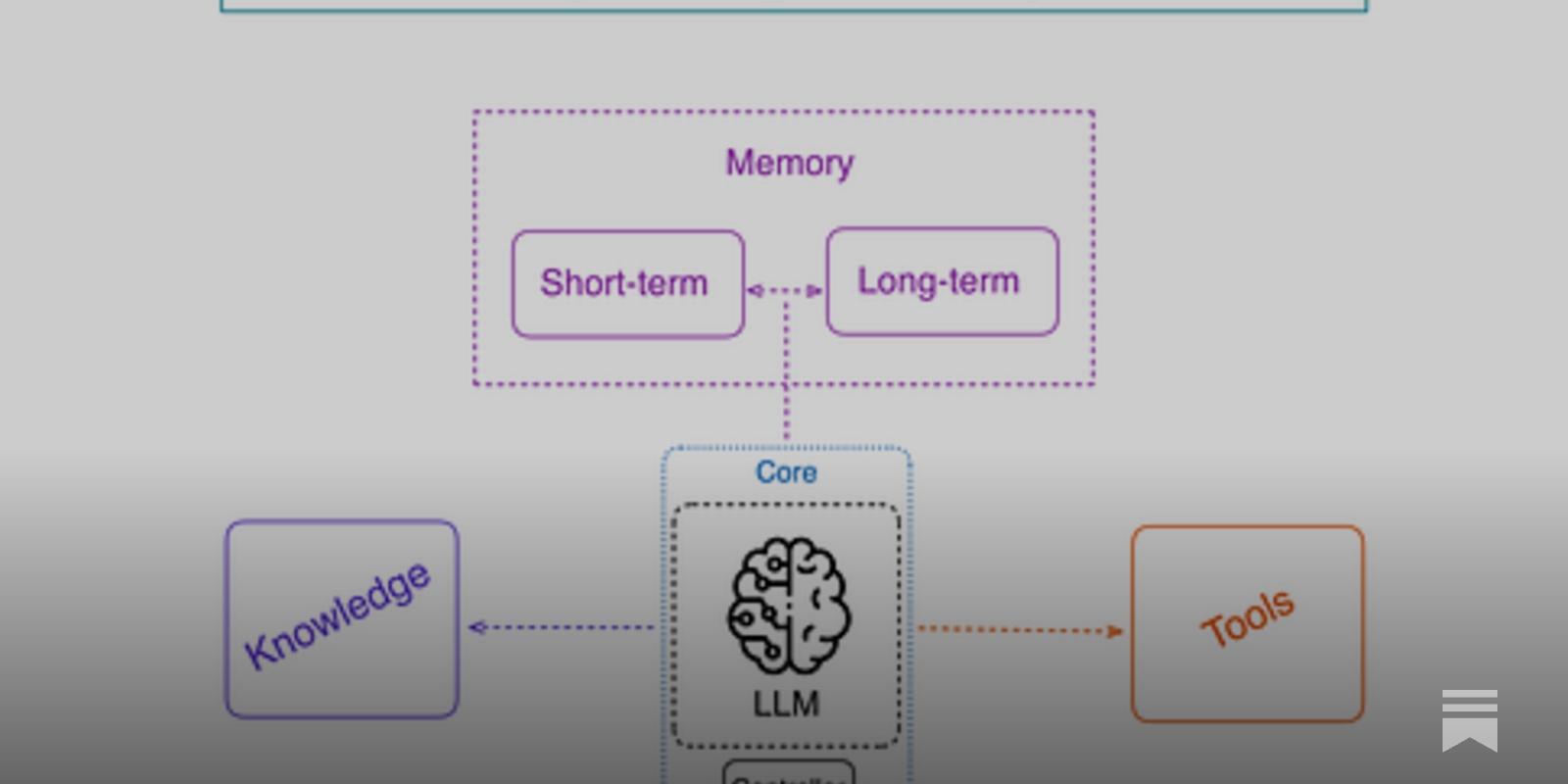
AI Memory Implementation
AI Memory Implementations
AI Memory Tools
AI Memory classified by Forms–Functions–Dynamics.
Agent memory is clearly distinguished from LLM memory, RAG, and context engineering.
- Forms: Token-level / Parametric / Latent memory
- Functions: Factual / Experiential / Working memory
- Dynamics: Formation–Evolution–Retrieval
Automation-centric design, RL integration, multi-modal/agent shared memory are challenges.

Working memory = Language Model Context
However, while LLMs use a fixed window of tokens, the human brain goes a step further by continuously updating a summary of past information to integrate longer-term context.
www.nature.com
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-56162-9
Large Language Models with Controllable Working Memory
Daliang Li, Ankit Singh Rawat, Manzil Zaheer, Xin Wang, Michal Lukasik, Andreas Veit, Felix Yu, Sanjiv Kumar. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023. 2023.
https://aclanthology.org/2023.findings-acl.112/

Mechanistic Analysis
arxiv.org
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.01014
However, while LLMs use a fixed window of tokens, the human brain goes a step further by continuously updating a summary of past information to integrate longer-term context.
Memory for agents
At Sequoia’s AI Ascent conference in March, I talked about three limitations for agents: planning, UX, and memory. Check out that talk here. In this post I will dive more into memory. See the previous post on planning here, and the previous posts on UX here, here, and here.
https://blog.langchain.dev/memory-for-agents/

Memory in Agent Systems
In this article I outline my thoughts on implementation of memory in GenAI systems.
https://www.newsletter.swirlai.com/p/memory-in-agent-systems
Vector Embeddings lacks Reference Frames for knowledge
LLM Memory
Some thoughts on implementations
https://grantslatton.com/llm-memory
AgeMem learns memory manipulation itself through RL. This difference means the model learns when/which memory actions are advantageous for long-term performance
arxiv.org
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.01885

 Seonglae Cho
Seonglae Cho