Diffusion Probabilistic model (DPM), Variational Diffusion Model
Diffusion models progressively add Gaussian noise to data (forward process) and learn to reverse this process step-by-step (reverse process). At high noise levels, the model recovers coarse, low-frequency structure; as noise decreases, it progressively refines the sample by adding higher-frequency details.
Diffusion models generate images by adding noise and then reversing it. Since white noise has energy across all frequencies but natural images have most energy in low frequencies, high-frequency components lose signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) first, making them harder to recover at early denoising steps.
Gradually add Gaussian noise with Markov Chain to model increasing noise process. Generate images by sampling from Gaussian noise. After that, the model learns to reverse noise into images by denoising process with modeling noise distribution. Due to Explicit likelihood Modeling, it solves the drawback of GAN where it covers less of the generation space.
Network Architecture
UNet like CNN image to image model is used as the reverse denoiser, often with Attention Mechanism during later compression/decompression stages such as Cross-Attention and image patches. Diffusion uses Positional Embedding for each time step. which prevents effective extrapolation like transformer do not.
Integral
The statement "denoising = integration" refers to the continuous-time perspective, where diffusion/flow-based generation is formalized as following the solution of a differential equation that continuously moves the state from noise to data. Rather than "removing noise all at once," it involves accumulating "small denoising actions" tens to thousands of times (through integral approximation) to create the final image.
Classic DDPM is a "discrete-time" Markov Chain that repeats denoising steps (step-by-step updates rather than integration), but from a continuous-time perspective, it ultimately connects to numerically solving the reverseSDE. DDIM / probability-flow ODE / flow matching / rectified flow approaches explicitly take the form of directly integrating an ODE from the start.
Diffusion Model Notion
Diffusion Model Usages
Diffusion Models
arxiv.org
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.11239
arxiv.org
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2105.05233
Tutorial
arxiv.org
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.18103
smalldiffusionyuanchenyang • Updated 2026 Feb 23 16:47
smalldiffusion
yuanchenyang • Updated 2026 Feb 23 16:47
Through noise prediction, we can mathematically prove that the denoiser can be viewed as an "approximate projection" onto the data manifold, equivalent to the gradient of a smoothed distance function (Moreau envelope). Gradient of a smoothed distance function to the manifold is equivalent as denoiser output, as a metaphor, trained denoiser generates force vectors that gradually bend towards the data manifold.
Then, DDIM can be interpreted as gradient descent, combining momentum and DDPM pddtechniques to improve convergence speed and image quality.
Diffusion models from scratch
This tutorial aims to give a gentle introduction to diffusion models, with a running example to illustrate how to build, train and sample from a simple diffusion model from scratch.
https://www.chenyang.co/diffusion.html
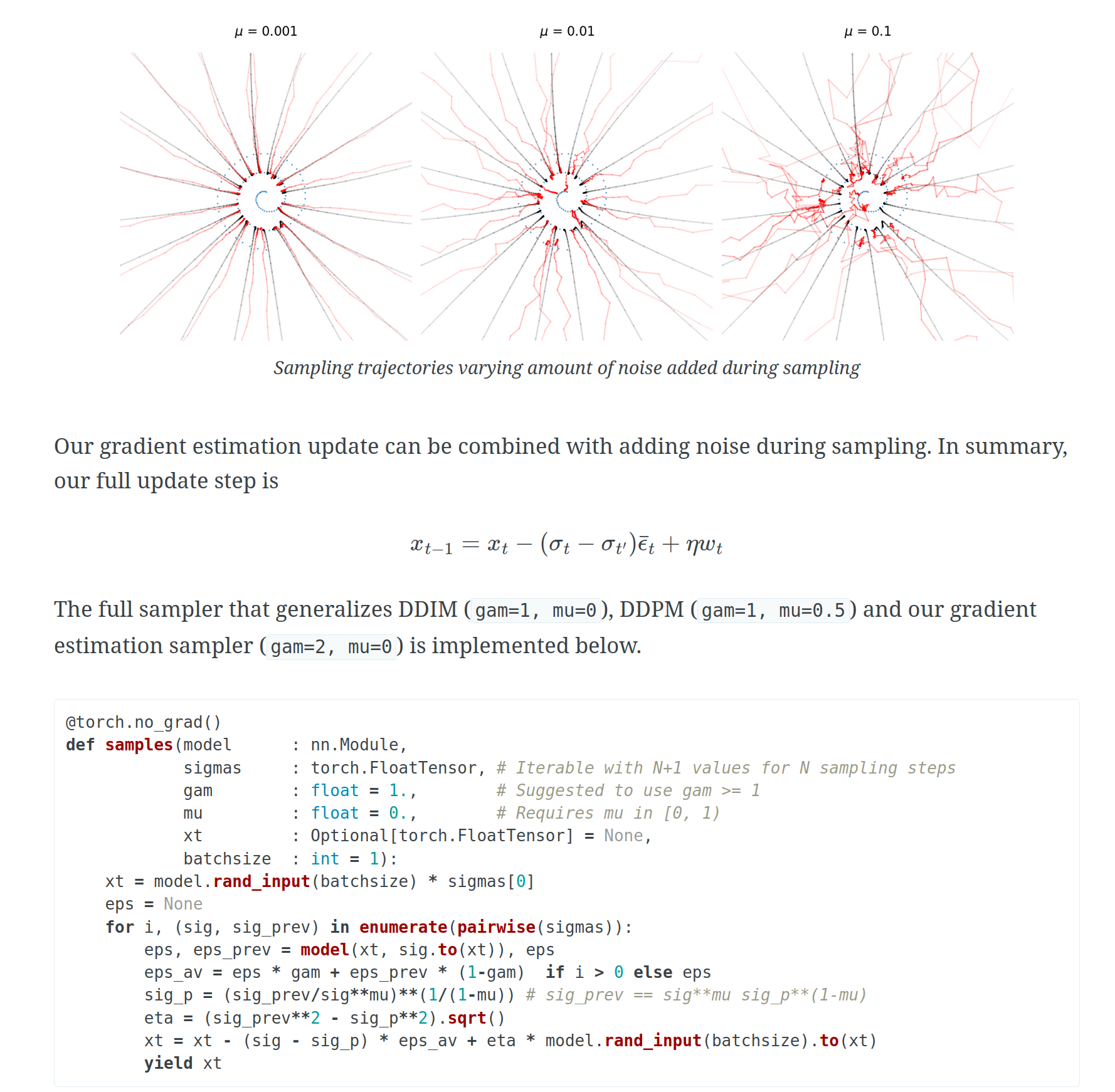
Interpreting and Improving Diffusion Models from an Optimization Perspective
Denoising is intuitively related to projection. Indeed, under the manifold hypothesis, adding random noise is approximately equivalent to orthogonal perturba...
https://proceedings.mlr.press/v235/permenter24a.html

 Seonglae Cho
Seonglae Cho